SEO vs. SEM: What’s the Difference, and Which One Is Right for You?
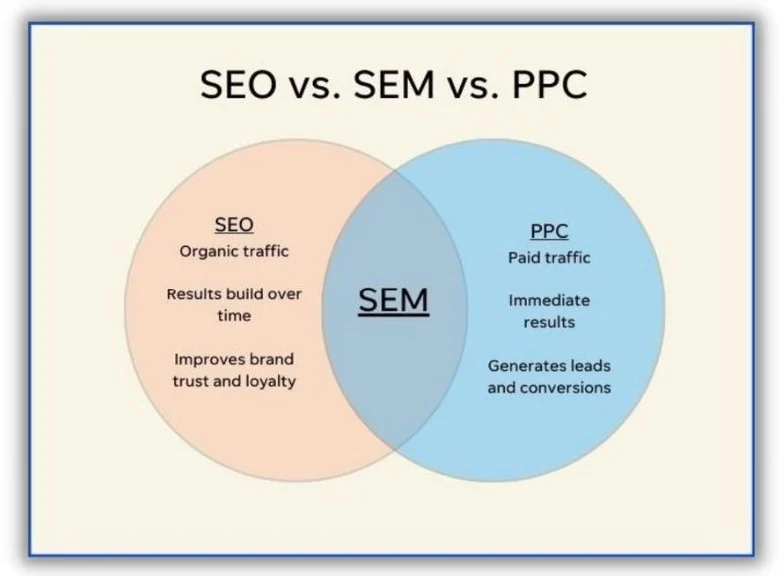
In today’s digital landscape, where visibility is everything, two acronyms seem to dominate the conversation: SEO and SEM. While both are essential for increasing traffic, they serve different purposes, involve different strategies, and can achieve different types of results. Let’s dive into what sets them apart and how each can benefit your business.
Which One Should You Choose?
Deciding between SEO and SEM depends on your business goals, budget, and timeline. Here’s a quick guide to help:
- If you need quick results: SEM is the way to go. Paid search ads give you immediate visibility and are a great option if you’re promoting a time-sensitive offer, such as a sale or new product launch.
- If you’re focused on long-term growth: SEO is your best bet. While it requires patience, a strong SEO strategy can bring steady, organic traffic over time, providing excellent ROI.
- If you have a mix of goals: A combined approach of SEO and SEM can be very effective. Using SEM to gain immediate traction while simultaneously investing in SEO for long-term traffic is a smart strategy many businesses adopt.
What is SEO? (Search Engine Optimization)
SEO is the art and science of improving a website’s visibility on search engines like Google without directly paying for it. In other words, SEO is about earning organic traffic—getting your site to appear higher in search results by optimizing content, improving user experience, and ensuring your site aligns with what search engines consider valuable and relevant.
Key Components of SEO:
- On-Page SEO: This focuses on optimizing individual pages on your website, including:
- Using relevant keywords
- Creating valuable, informative content
- Optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, and image alt texts
- Off-Page SEO: Off-page efforts aim to build your site’s authority and trustworthiness through:
- Earning backlinks from reputable sites
- Encouraging social sharing and brand mentions
- Technical SEO: The technical side of SEO focuses on your website’s infrastructure:
- Enhancing site speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- Creating a logical site structure for better crawlability
The Goal of SEO:
The main goal of SEO is to improve rankings in organic (unpaid) search results. Although SEO requires a considerable amount of time to see results, it’s a long-term investment that can yield steady, sustainable traffic.
What is SEM? (Search Engine Marketing)
SEM, on the other hand, includes paid advertising efforts to make your site more visible on search engine results pages (SERPs). The primary focus of SEM is on Pay-Per-Click (PPC) ads that appear above or alongside organic search results. SEM strategies typically involve platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads, where you bid on keywords to display ads to users searching for those terms.
Key Components of SEM:
- Keyword Research and Targeting: Just like with SEO, keyword research is crucial for SEM. However, the approach differs in that you select keywords based on bidding strategies and competition level.
- Ad Creation: SEM involves crafting compelling ad copy that encourages clicks. A well-designed ad might include:
- A catchy headline
- Relevant keywords
- A call-to-action (CTA) that prompts users to take the next step
- Bid Management and Budgeting: With SEM, you set a budget for your campaigns. You pay each time a user clicks on your ad, so managing bids is essential to make the most of your budget.
- Performance Tracking and Optimization: SEM allows for precise targeting and provides detailed insights on performance, allowing for real-time adjustments. You can track:
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Conversion rate
- Cost-per-click (CPC)
The Goal of SEM:
The primary goal of SEM is to drive targeted traffic quickly by paying for ad placement on SERPs. It’s ideal for businesses looking to see immediate results, as SEM ads can start bringing traffic as soon as the campaign is launched.